
What is Usability Testing? UX(User Experience) Testing Example
Usability Testing
Usability Testing also known as User Experience(UX) Testing, is a testing method for measuring how easy and user-friendly a software application is. A small set of target end-users, use software application to expose usability defects. Usability testing mainly focuses on user’s ease of using application, flexibility of application to handle controls and ability of application to meet its objectives.
This testing is recommended during the initial design phase of SDLC, which gives more visibility on the expectations of the users.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
- What is Usability Testing?
- Why do Usability Testing
- Example Usability Testing Test Cases
- How to do Usability Testing: Complete Process
- Methods of Usability Testing: 2 Techniques
- How many users do you need?
- UX Testing Checklist
- Usability Testing Advantages
- Usability Testing Disadvantages
Why do Usability Testing

Aesthetics and design are important. How well a product looks usually determines how well it works.
There are many software applications/websites, which miserably fail, once launched, due to following reasons –
- Where do I click next?
- Which page needs to be navigated?
- Which Icon or Jargon represents what?
- Error messages are not consistent or effectively displayed
- Session time not sufficient.
Software Engineering, Usability Testing identifies usability errors in the system early in the development cycle and can save a product from failure.
Example Usability Testing Test Cases
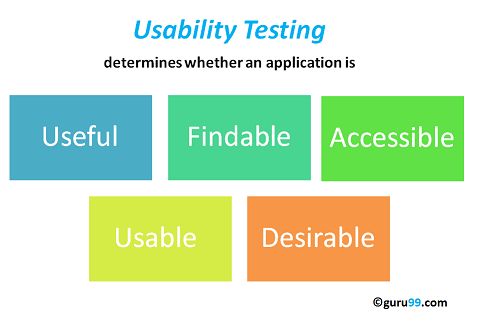
The goal of this testing is to satisfy users and it mainly concentrates on the following parameters of a system:
The effectiveness of the system
- Is the system is easy to learn?
- Is the system useful and adds value to the target audience?
- Are Content, Color, Icons, Images used are aesthetically pleasing?
Efficiency
- Little navigation should be required to reach the desired screen or webpage, and scrollbars should be used infrequently.
- Uniformity in the format of screen/pages in your application/website.
- Option to search within your software application or website.
Accuracy
- No outdated or incorrect data like contact information/address should be present.
- No broken links should be present.
User Friendliness
- Controls used should be self-explanatory and must not require training to operate
- Help should be provided for the users to understand the application/website
- Alignment with the above goals helps in effective usability testing
How to do Usability Testing: Complete Process
Usability testing process consists of the following phases
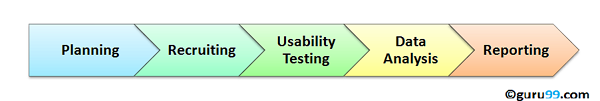
Planning:- During this phase the goals of usability test are determined. Having volunteers sit in front of your application and recording their actions is not a goal. You need to determine critical functionalities and objectives of the system. You need to assign tasks to your testers, which exercise these critical functionalities. During this phase, the usability testing method, number & demographics of usability testers, test report formats are also determined
Recruiting: During this phase, you recruit the desired number of testers as per your usability test plan. Finding testers who match your demographic (age, sex etc.) and professional ( education, job etc.) profile can take time.
Usability Testing: During this phase, usability tests are actually executed.
Data Analysis: Data from usability tests is thoroughly analyzed to derive meaningful inferences and give actionable recommendations to improve the overall usability of your product.
Reporting: Findings of the usability test is shared with all concerned stakeholders which can include designer, developer, client, and CEO
Methods of Usability Testing: 2 Techniques
There are two methods available to do usability testing –
- Laboratory Usability Testing
- Remote Usability Testing
Laboratory Usability Testing:. This testing is conducted in a separate lab room in presence of the observers. The testers are assigned tasks to execute. The role of the observer is to monitor the behavior of the testers and report the outcome of testing. The observer remains silent during the course of testing. In this testing, both observers and testers are present in a same physical location.
Remote Usability Testing: Under this testing observers and testers are remotely located. Testers access the System Under Test, remotely and perform assigned tasks. Tester’s voice , screen activity , testers facial expressions are recorded by an automated software. Observers analyze this data and report findings of the test. Example of such a software – http://silverbackapp.com/
How many users do you need ?

Research (Virzi, 1992 and Neilsen Landauer, 1993) indicates that 5 users are enough to uncover 80% of usability problems. Some researchers suggest other numbers.
The truth is , the actual number of the user required depends on the complexity of the given application and your usability goals. Increase in usability participants results into increased cost , planning , participant management and data analysis.
But as a general guideline, if you on a small budget and interested in DIY usability testing 5 is a good number to start with. If budget is not a constraint its best consult experienced professionals to determine the number of users.
UX Testing Checklist
The primary goal of this testing is to find crucial usability problems before the product is launched. Following things have to be considered to make a testing success:
- Start the UX testing during the early stage of design and development
- It’s a good practice to conduct usability testing on your competitor’s product before you begin development. This will help you determine usability standards for your target audience
- Select the appropriate users to test the system(Can be experts/non-experts users/50-50 of Experts and Non-Experts users)
- Use a bandwidth shaper . For instance , your target audience has poor network connectivity , limit network bandwidth to say 56 Kbps for your usability testers.
- Testers need to concentrate on critical & frequently used functionalities of the system.
- Assign a single observer to each tester. This helps observer to accurately note tester’s behavior. If an observer is assigned to multiple testers, results may be compromised
- Educate Designers and Developers that this testing outcomes is not a sign of failure but it’s a sign of Improvement
Usability Testing Advantages
As with anything in life, usability testing has its merits and de-merits. Let’s look at them
- It helps uncover usability issues before the product is marketed.
- It helps improve end-user satisfaction
- It makes your system highly effective and efficient
- It helps gather true feedback from your target audience who actually use your system during a usability test. You do not need to rely on “opinions” from random people.
Usability Testing Disadvantages
- Cost is a major consideration in usability testing. It takes lots of resources to set up a Usability Test Lab. Recruiting and management of usability testers can also be expensive
However, these costs pay themselves up in form of higher customer satisfaction, retention and repeat business. Usability testing is therefore highly recommended.




0 Response to "What is Usability Testing? UX(User Experience) Testing Example"
Post a Comment