What is Parallel Testing? Definition, Approach, Example
Parallel Testing
Parallel Testing is a software testing type in which multiple versions or subcomponents of an application are tested with same input on different systems simultaneously to reduce test execution time. The purpose of parallel testing is finding out if legacy version and new version are behaving the same or differently and ensuring whether new version is more efficient or not.
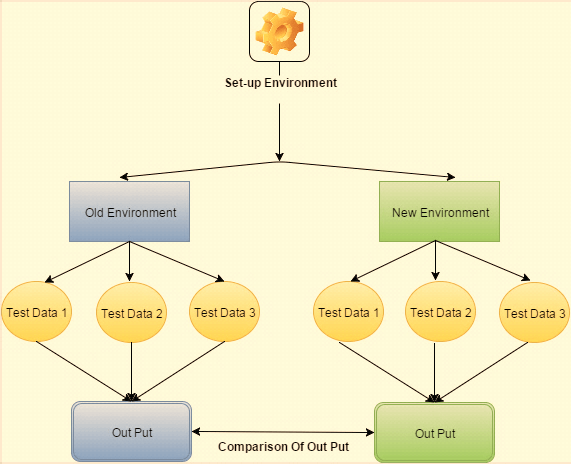
The below image demonstrate the parallel testing.

Parallel Testing Example
When any organization is moving from old system to new system, legacy data is an important part. Transferring this data is a complex process.
In software testing, verifying compatibility of the newly developed system with the old system is done through “parallel testing.”

Why to do Parallel Testing
Parallel Testing is done due to following reason,
- To make sure the new version of the application performs correctly
- To make sure the consistencies are same between new and old version
- To check if the data format between two versions has changed
- To check the integrity of the new application
For example- currently users are using 1.0 version of an application and from the month of March users are going to use another version of an application, let’s say 1.1 version.

In such cases, testers need to do the parallel testing, in order to evaluate that data migration is done successfully. Also to check whether the changes in the new version does not affect the system function. The tester must verify that changes are executed properly, and the user is getting the desired output as per the requirement.
When to do Parallel Testing
Parallel testing can be used extensively when
- The company moving from old system to new system
- When synchronization is performed on two systems
- Legacy data imported from one system to another
- All the outcomes should be defined more precisely. Example, financial domain or insurance domain where the calculation is a major functionality of the system.
How to do Parallel Testing: Complete Approach
For performing parallel testing, you can simply create several project that will test a different part of the application (Slave Projects) and one project (master project) that will run these projects.
Parallel Testing has two level criteria.
- Parallel test entry Criteria
Parallel test entry criteria define the tasks that must be satisfied before parallel testing can be efficiently executed.
- Parallel test exit Criteria
Parallel test exit criteria defines the successful conclusion of the parallel testing stage.
Before performing parallel testing, there are few pre-condition that has to be satisfied.
- Parallel test cannot begin till environment setup is done.
- All pre-conditions and scenarios should be defined first
- Legacy data and new data must be migrated successfully
- Parallel test is not complete until all of the exit criteria have been satisfied
To perform Parallel Testing, following steps should be followed
Step 1: Run old system against newly developed system
Step 2: Understand different between both the system
Step 3: Go throw complete cycle using same input
Step 4: Measure the output of newly developed system compare to the old system
Step 5: Report cause of bug if found
Good Practices for Parallel Testing
To perform parallel testing here are few tips and tricks, which might be useful.
- Typical bugs identified in Parallel Testing
Internal logic is changed
Flow of product is changed
Major functionalists are modified
- How Many Cycles Should Be Required
Number of testing cycle depends upon the complexity of the module.
Run multiple scenario cycles using pre-defined test data, which was pass from the previous system
- Categorizing Difference
When we run the parallel testing cycle, the results of both the new and legacy systems should be measured line by line with differences highlighted. Every difference which we captured should be defined as per the type of error.
- Type of error occurred during cycles
For errors tester should note down following things while performing parallel testing.
- Entry error
- Error due to the old system
- Explainable or acceptable different
- Unexpected error
What is not a Parallel Testing
| It is Parallel Testing | It is not Parallel Testing |
|---|---|
|
|
Challenges of Parallel Testing
- Complete product knowledge is required.
- Every outcome should be tested
- Need to concentrate on Data input and flow of product
Summary:
- In Software Engineering, Parallel testing is testing multiple applications or subcomponents of one application concurrently to reduce the test time.
- It ensures that the new system is capable enough to run the software efficiently.




0 Response to "What is Parallel Testing? Definition, Approach, Example"
Post a Comment